 AEROBOTICS ARCHIVE
AEROBOTICS ARCHIVE
 AEROBOTICS ARCHIVE
AEROBOTICS ARCHIVE

Image Capture and FMA 'Co-Pilot' TrialsNovember 15, 2001
The Monash Aerobotics team are currently experimenting with different types of R/C aircraft platforms for the capture air to ground stills and video. Under test this day using the Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" ("LH") was a combination of a live video feed from "LH" as a visual guide to the capture of still images on a separate onboard 3.1 megapixel digital camera (Nikon Coolpix900 - shown below) that were mapped to a given GPS location. Also this day we employed a new miniature flight stabilization system known as 'Co-Pilot' which was first trialled on "LH" and later in the day, on a 2.5m, non-powered, 'flying wing' sailplane designed and built by Professor John Bird.
FMA Direct's 'Co-Pilot' is a patented system that senses the difference in infrared signature between the earth and the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to provide 100% real time, day or night stabilization about two axes on any 'model'." ...more on October 11, 2002, Brian Taylor wrote...
'Co-Pilot' certainly works very well but we (the Aerobotics@Monash team) suggest does not rely on carbon dioxide in the atmosphere but instead is ruled by Planck's Law for blackbody radiation. Please note: As this page was being compiled it was discovered a fault had occurred in the still image capture process and the images were unusable. In the spirit of research we still present the still image plans of this trial day - and promise to do better next time - promise ! For those new to this programme, it is important to note that the 'Monash' Aerosonde (a Mk1), unlike the current (Mk.3) autonomous production model flies under model aircraft regulations rather than those imposed by CASA, the Civil Aviation Safety Authority of Australia. Although limiting the craft to a ceiling of 300 feet, flying under 'manually directed' model aircraft regulations, allows the Monash team to conduct trials at times to suit the sometimes irregular 'academic' schedule. This less formalised trials activity is also made possible via a relationship established with VARMS who allow the Monash team the use of their nearby flying field. It is worth noting that in 1998, 'Laima', a sister craft to Monash's Aerosonde 'Lawrence Hargrave', was the first robotic aircraft to fly the Atlantic Ocean.
Hardware Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
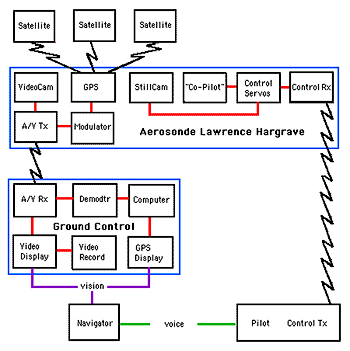 Schematic Theoretical Download a 500pixel image
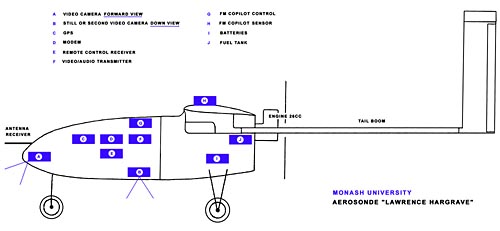 Schematic Practical Download a 1000pixel image
 Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" equipment bay Download a 500pixel image
 Nikon CoolPix900
 Nikon CoolPix900 showing cradle and downward facing lens Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Nikon CoolPix900 showing cradle and servo operated shutter release Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
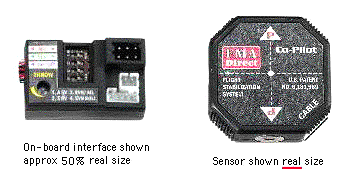 FMA Direct's 'Co-Pilot' Specifications: Inputs aileron, elevator, and aux for Remote switched or fully proportional Enable from the receiver; outputs pitch (elevator) and roll (aileron or rudder) via normal servo cables; system weight 1.00 ounces; sensor dimensions 1.35" (octagonal) by 0.53" thick; microprocessor 1.50" x 0.89" x 0.60"; power consumption 5 ma. ...more
 FMA Direct's 'Co-Pilot' fitted to Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Preparing to launch Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" L-R : Prof. Greg "Biggles" Egan, Prof. John Bird and Chief Pilot, Ray Cooper Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Prof. Greg "Biggles" Egan testing the "Co-Pilot" in flight L-R : Prof. John Bird, Prof. Greg "Biggles" Egan and Chief Pilot, Ray Cooper Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Video and Comms. specialist Terry Cornall watching the progress of the flight on a GPS display Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
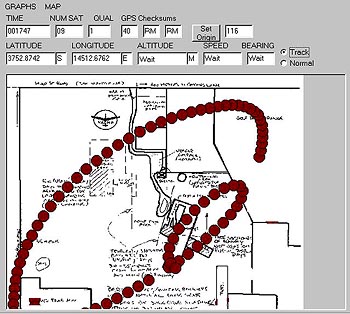 Screen shot of the GPS display The image shows Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" mapped on an image of the immediate area below at a rate of one 'blip' per second. GPS measurements were taken using a 600 Baud AFSK telemetry modem (connected to the audio channel of the video transmitter on Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave") and transmitting data to the field laptop computer. Download a 500pixel image
 Mission IT Support, Paul Jenkins and Ian Reynolds Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 On high : the team keeping an eye on Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" L-R : Prof. John Bird, Chief Pilot Ray Cooper, Prf. Greg "Biggles" Egan and project supporter, television specialist Peter Cossins Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 A soulmate for Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" : a wedgetailed eagle soars within a few hundred feet - wayyyyy up there in the blue. the downloadable images show the eagle slightly more clearly. Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" comes into land using the FMA Direct 'Co-Pilot' Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Chief Pilot Ray Cooper taxis Aerosonde "Lawrence Hargrave" back to the pits. Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
Trialling the FMA Direct 'Co-Pilot' with a Flying Wing Installing the FMA Direct 'Co-Pilot' on Prof. John Bird's flying wing Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Prof. John Bird with his flying wing complete with FMA Direct 'Co-Pilot' installed Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Close up of FMA Direct 'Co-Pilot' installed on Prof. John Bird's flying wing Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
 Prof. Greg "Biggles" Egan bungee launches Prof. John Bird's flying wing Download a 500pixel or 1000pixel image
|
Return to Aerobotics
The term Aerobotics is Copyright © 1999-2007, CTIE